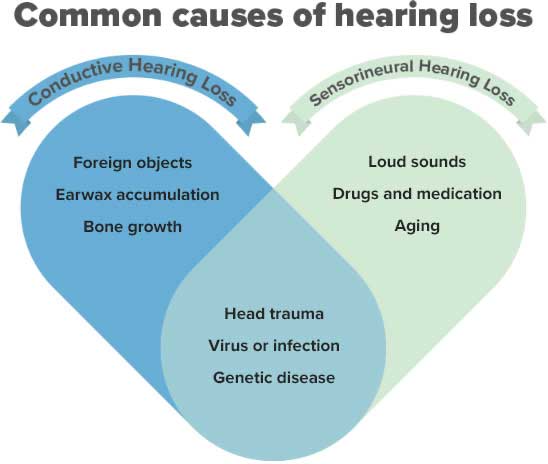
What are the main types of hearing loss?
The main types of hearing loss are differentiated based on which part of the ear is damaged:
- Sensorineural hearing loss caused by damage to the inner ear or hearing nerve. This prevents the damaged area from properly transmitting sound to the brain.
- Conductive hearing loss is caused by damage in the external and/or middle ear and, in most cases, it is medically treatable.
- Mixed hearing loss - In some cases, both aspects of sensorineural and conductive hearing loss are present; this is referred to as mixed hearing loss.